Drug or Nutrient Delivery Systems
- Home
- RESEARCH
- Drug or Nutrient Delivery Systems
Drug or Nutrient Delivery Systems
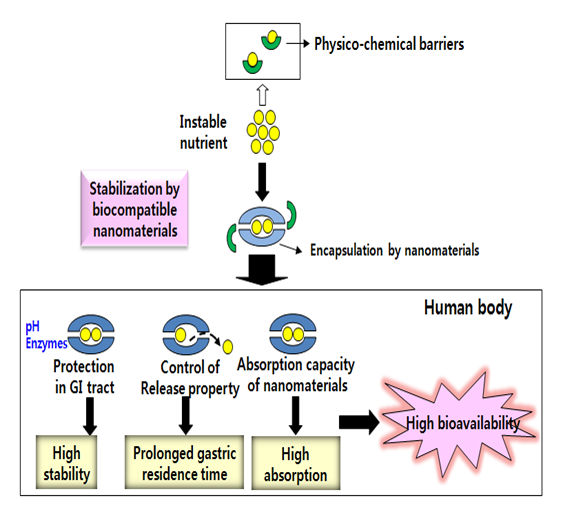
Nutrient intake with high bioavailability represents a formidable challenge, because only a small proportion of molecules remain available following oral intake. There are several factors that influencing low bioavailability: insufficient gastric resident time, low permeability, low solubility within the gut, instability during food processing (temperature, oxygen, light) or in the gastro-intestinal (GI) tract (pH, enzymes, presence of other nutrients).
The concept of “Nutrient delivery system (NDS)” using nanomaterials is to develop protective mechanisms that maintain the active molecular form until the time of consumption and deliver this form to the physiological target organs. Various nanotechniques such as nanohybridization , emulsification and encapsulation can be applied for storing and protecting fragile functional ingredients such as vitamins, aroma, nutrients, colorants and etc. Encapsulated instable nutrients can be protected during food processing and preservation, released in a controlled manner, giving rise to increase gastric residence time, and absorbed effectively due to high absorption capacity of nanomaterials themselves to the gut, all of which increase high bioavailability in biological systems.
